Meaning of Psychology
Psychology is defined as the investigation, observation, and interpretation of the mind and behavior. There are various classification of psychology. Psychology encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including abnormal psychology, clinical psychology, counseling psychology, developmental psychology, forensic psychology, personality psychology, and social psychology. Individuals must understand psychology categorization because of the ongoing trend of individuals studying, learning, and working in the psychology profession during the next 10 years.

However, if people do not understand whether psychology is supported as a science or not, it is possible that they may have feelings of perplexity. A professional psychologist will meet with patients, do evaluations to determine their concerns and the source of any problems, and then propose or give treatment, such as counseling and psychotherapy.
Psychologists may also have other responsibilities. They may do research to advise health authorities and other agencies on social and other measures, engage with corporate recruitment teams, assess children who struggle to study in school, deliver courses on how to prevent bullying, etc.
Classification of Psychology
There are various kinds of psychology that serve various goals. There is no defined way to categorise them, though several common categories are present.
Clinical Psychology
The first classification of psychology is Clinical psychology combines science, theory, and practice to better understand, anticipate, and treat issues related to adjustment, impairment, and discomfort. It encourages adaptation, adjustment, and personal growth. A clinical psychologist focuses on the cognitive, emotional, biological, psychological, social, and behavioral elements of human performance throughout one’s life, across cultures and socioeconomic levels.
Clinical psychology can assist us in understanding, preventing, and alleviating psychologically generated suffering or dysfunction, as well as promoting an individual’s well-being and personal development.
The practice of clinical psychology is fundamental to psychological evaluation and treatment, however often clinical psychologists are involved in research, training, forensic evidence and other areas as well.
Neuropsychology
it is the study of the structure and function of the brain in connection to psychological processes and behaviours. If a disorder involves brain lesions and tests that include monitoring electrical activity in the brain, neuropsychology may be involved.

Following a suspected or diagnosed brain damage, such as a stroke, a neuropsychological test is done to evaluate whether a person is likely to have behavioral issues. The evaluation may enable a doctor to prescribe treatment that will help an individual in reversing any occurred cognitive damage.
Counseling Psychology
Counseling psychology is one of the most important areas in psychology. It focusses on treating clients with a wide range of psychological symptoms and mental anguish. It also focuses on employing psychological concepts to improve and promote the positive growth, well-being, and mental health of people, families, groups, and the larger community.

The Psychology Society of Counseling identifies the topic as a field in which interpersonal functions can be improved throughout life by enhancing social and emotional health, as well as addressing health, job, family, marriage and more.
Developmental Psychology
The field of developmental psychology studies how people evolve and evolve throughout their lives. Human development science tries to understand and explain how and why people evolve throughout their lives. Physical growth, intellectual development, emotional changes, social growth, and perceptual changes are all topics that developmental psychologists investigate throughout the course of a lifetime.

These psychologists typically specialize in a specific area of development, such as baby, child, adolescent, or geriatric development, however others may examine the impact of developmental delays. This discipline encompasses a wide range of topics, from prenatal development through Alzheimer’s illness.
Abnormal Psychology
Abnormal psychology is a discipline of psychology that investigates atypical patterns of behavior, emotion, and thinking that could be interpreted as a mental condition. Although many behaviors might be classified as aberrant, this discipline of psychology focuses on behavior in a clinical setting. The area of abnormal psychology looks for many causes for various illnesses, drawing on a variety of theories from psychology and other fields, and much still depends on what exactly is meant by “abnormal.”

Adaptive and maladaptive behaviors are the two categories of behaviors studied in abnormal psychology.
Maladaptive behaviors indicate the presence of a problem(s) and can also indicate that the individual is weak and unable to cope with environmental stress, resulting in difficulties functioning in daily life in terms of emotions, mental thinking, physical actions, and communication. Adaptive behaviors are those that are well-suited to people’s natures, lifestyles, and environments, as well as the people with whom they communicate, allowing them to understand each other.
Health Psychology
The next important classification of psychology is health psychology is a branch of psychology that studies how biology, psychology, behavior, and social factors interact to determine health and illness. Other concepts, such as medical psychology and behavioral medicine, are occasionally used interchangeably with the word health psychology. Health psychology is concerned with the encouragement to health as well as the prevention and treatment of diseases and illness. These experts work on both the prevention and treatment of illness and disease, as well as promoting healthy behaviors.

Weight control, smoking cessation, stress management, and nutrition are among concerns that health psychologists deal with on a regular basis. They may also do research into how people cope with illnesses and assist patients in developing new, more effective coping mechanisms. Some professionals in this field assist in the development of public awareness and prevention programs, while others work for the government to enhance health-care policies.
Organizational Psychology
Organizational or Occupational psychologists examine and make recommendations on people’s performance at work and in training. They help businesses in finding more efficient ways to operate and in understanding how a person or a group behaves at work.

This data can help in escalating productivity, efficiency, work happiness, and staff retention.
Educational Psychology
The branch of psychology concerned with schools, teaching psychology, educational challenges, and student concerns is known as educational psychology. Educational psychologists frequently investigate how students learn or collaborate with students, parents, teachers, and administrators to enhance student outcomes.
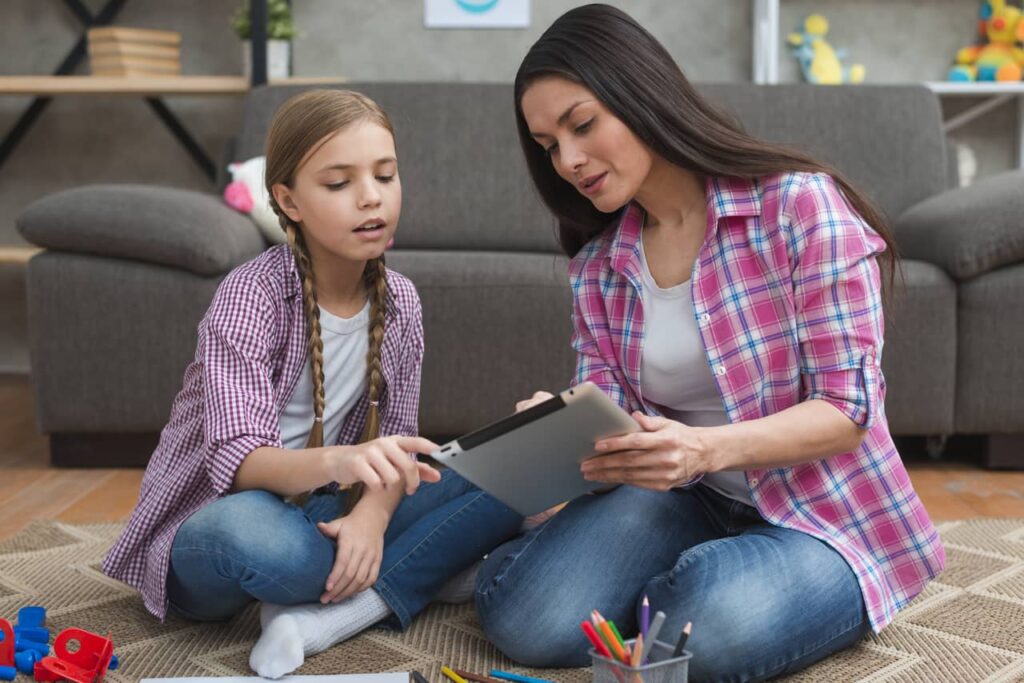

They could look into how various variables affect individual student outcomes. Learning impairments, giftedness, the teaching method, and individual differences are among the issues they research.
Forensic Psychology
The next classification of psychology is forensic psychology is a subfield of psychology that deals with legal and psychological difficulties. Psychological principles are applied to legal concerns by those who work in this discipline of psychology. This may entail researching criminal behavior and therapies, as well as working directly in the court system. Forensic psychologists have a wide range of responsibilities, including testifying in court, screening children in suspected child abuse cases, preparing minors to testify, and assessing the mental competency of criminal suspects.

This branch of psychology is characterized as the junction of psychology and the law, however because forensic psychologists can perform a variety of functions, this definition is subject to change.
In many circumstances, forensic psychologists are not necessarily “forensic psychologists”. These people could be clinical psychologists, neurologists, school psychologists, or counsellors who use their psychological knowledge to provide analysis, testimony, or suggestions in criminal or legal proceedings.
Sports Psychology
Sport psychology is an interdisciplinary study that draws on knowledge from a variety of disciplines, including biomechanics, physiology, kinesiology, and psychology. It entails the investigation of how psychological elements influence performance, as well as how involvement in sports and exercise influences psychological and physical aspects.

Athletes are taught cognitive and behavioral tactics by sport psychologists in order to improve their experience and performance in sports.
Applied sport psychology can include work with athletes, Coaches and Parents on injuries, rehabilitation, communications, team building and career transitions, as well as training in and education on psychological skill to increase performance.
Sports psychiatry is also strongly linked.
Cognitive Psychology
Internal mental processes, for example, problem solving, learning, memory, and language are studied in cognitive psychology. It examines people’s thinking, perceptions, connections, memory, and studying. Neuroscience, philosophy, and linguistics are all tightly interconnected.

Cognitive psychologists study how people collect, analyze, and store data. How to strengthen memory, increase decision-making precision, or put up educational programs to boost learning are some of the practical uses.
Experimental Psychology
Experimental psychology is a discipline of psychology that studies the brain and behavior using scientific methods. Many of these techniques are also utilized in other branches of psychology to study everything from early development to social issues. Experimental psychologists work in a number of settings, including colleges, universities, research institutes, government agencies, and commercial companies.

Experimental psychologists explore a wide spectrum of human behaviors and psychological phenomena using the scientific approach. Although this subject of psychology is frequently thought of as a separate subfield, experimental procedures and procedures are employed extensively in every discipline of psychology.
Experiments, correlational studies, case studies, and naturalistic observation are some of the approaches employed in experimental psychology.
Social Psychology
The last classification of psychology is social psychology. To study how social forces, influence human behavior, social psychology employs scientific approaches. It aims to explain how the actual, suggested, or imagined presence of other people affects one’s feelings, thinking, and behavior. Group behavior, social perception, abidance, nonverbal behavior, violence, prejudice, and leadership are all examined by a social psychologist.

Grasp social conduct requires an understanding of social interaction and perception. Some of the other disciplines of psychology are military, environmental psychology, consumer, cross-cultural, and educational. The number of branches is increasing.
Further Reading:









